An Overview of the Types of Electronic Measurement Devices
Contents
– Electronic measuring instrument: Characteristics
– Types of electronic measuring devices
– Electronic measuring instruments: prices and distribution
An electronic measuring device is a compact tool that allows data collection for a particular study.
Electronic measuring instrument: Characteristics
An electronic measuring device allows the easy measurement of a distance, a volume, a quantity, or any other measurable value, such as a current, chemical composition, or sound.
Depending on the nature of what is to be measured and the objective of the measurement, the electronic device is compact, mobile, or fixed. Depending on the use of the device, the characteristics vary buzzer (measured in dB); operating temperature (expressed in degrees Celsius); humidity level (%); air content (ppm, point per million for gases); digital screen (precise data reading); memory (frequent readings, curve); calculator (average); warning light (LED), etc. The complexity of use is related to its functionalities, such as the expertise required to read the transmitted data.
Please note: electronic measuring devices operate on batteries (rechargeable or not) or a battery (usually Lithium-ion), integrated or not in the machine.
Types of electronic measuring devices
The measuring devices have different names, depending on the nature of what they measure. They are used in industry, mechanics, construction, home, or for specific meteorological purposes.
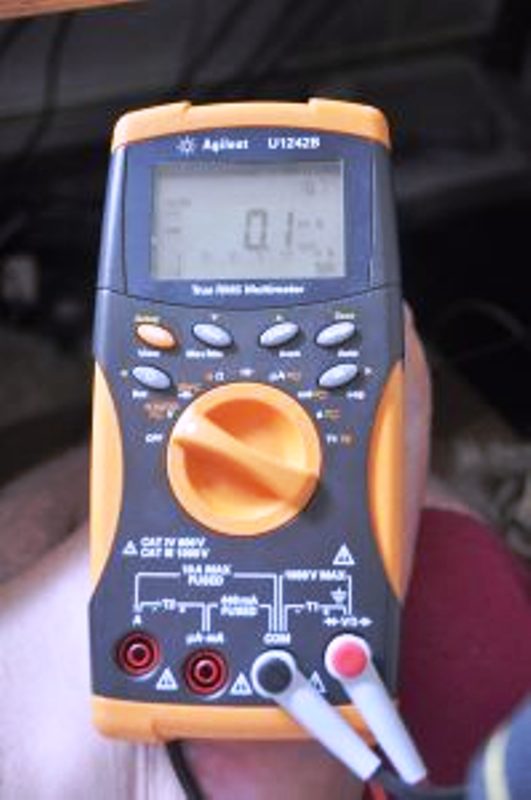
– A multimeter measures electrical quantities (volts, ohms, amperes): it is an essential tool in electricity.
– A manometer expresses pressure in bars (B); it is useful in pneumatics, among others.
– A telemeter measures a distance; it can be laser or ultrasound combined with a cell for a remote reading (building and construction).
– A tachometer determines the rotation speed: it is used in industry.
– A micrometer measures the thickness of a solid body.
– A sound level meter expresses the number of decibels (dB) and allows noise exposure.

– A pH meter evaluates the potential hydrogen content in a liquid or the ground; private individuals and pool specialists mainly use it for swimming pools.
– A clock measures time and is mainly used in the sports world.
Four primary devices carry out the study of the weather.
– A thermometer measures the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit (F) or Celsius (°C); it is used indoors or outdoors.
– A hygrometer evaluates the humidity level; it is helpful in nurseries, the study of climate, and even the home.
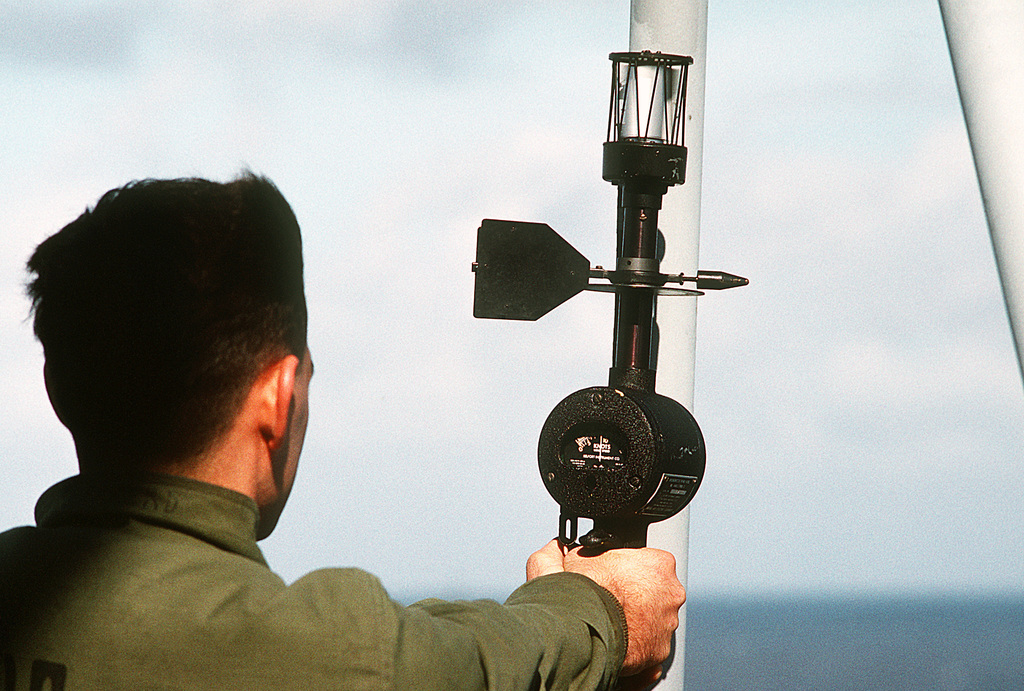
– An anemometer measures wind strength, expressed in knots, km/h, or using the Beaufort scale.
– A rain gauge measures the rate of precipitation, expressed in mm (millimeters).
Note: There are as many measuring devices as values to be measured.
Electronic measuring devices: price and distribution
Depending on their type, measuring devices are sold by DIY stores, specialized distributors (sanitary and industrial), and the Internet. The price range is vast and depends on the device and its quality. Count:
– about $50 for a pH meter with automatic calibration;
– $60 for a laser rangefinder with a 30 m range;
– $90 for a weather station with a rain gauge, thermometer, and anemometer included;
– $250 for a mid-range tachometer for professional use.
Did you like this post? Read this post: How to Calculate Your Electrical Power for even more measuring instruments, but this time, electrical ones like the voltmeter, ammeter, multimeter, and more.
Read more:
– What Is the Heating Flow Temperature of a Heat Pump (Part 1)?
– What Is the Heating Flow Temperature of a Heat Pump (Part 2)?
– How to Choose between a High or Low-Temperature Heat Pump?
– What Are the 2 Operating Modes of a Heat Pump?

