Before buying your boiler, you must first estimate your needs, choose among different energies, and finally determine the boiler model, which will affect both budget and efficiency. This post helps you make the right choice.
Summary
– The operation of a boiler
– Criteria of choice
– Types of boiler: which energy to choose?
– Condensation or low temperature: which technology to choose?
How a boiler works
The boiler is the engine of your central heating system. Whatever the fuel used, its role is to supply the heat emitters (radiators, underfloor heating, or fan coil units). This post talks about the boiler’s operating principle and the associated distribution system.
Selection criteria
There are many more needs to assess before choosing a boiler than you might think. If you have to replace your boiler in an emergency following a breakdown, take the time to study the available solutions. Changing your boiler can be an opportunity to question your energy choice and save money.
Your situation
Start by considering your situation: the type of housing (apartment or house, for example), its volume and the number of inhabitants, and your home insulation, which will generate more or less heat loss.
The power
The boiler’s power affects its ability and speed to supply the dwelling with hot water, whether it is for heating only or also for domestic hot water. This power, therefore, depends on your needs and the surface area of the dwelling.
Hot water production
The boilers can be used for heating alone, without hot water production, if you already have an independent water heater. You can also opt for a boiler that will provide both heating and domestic hot water production, either instantly or with an accumulator tank.
Floor or wall-mounted boiler?
Wall-mounted, the boiler is easy to install, it is generally less powerful and therefore recommended for apartments or small houses. On the floor, it is larger and more powerful.
Types of boilers: which energy to choose?
Each energy has its characteristics, which will influence your boiler’s purchase price and its installation, operating costs, and performance.
The oil-fired boiler

The oil-fired boiler diffuses heat quickly and today benefits from the latest technologies (condensation, low temperature) to offer excellent efficiency. However, this type of boiler requires a storage tank for fuel oil.
The gas boiler
The gas boiler can be connected to city gas or be fueled with propane gas, then stored in a tank with its disadvantages. In either case, the gas boiler is very efficient.
The wood boiler
The wood boiler uses wooden logs and pellets. With wood logs, the boiler must be fed manually and has only a few hours of autonomy, whereas, with pellets, the feed can be automatic.
The electric boiler
Easy to install and to connect to electricity, the electric boiler is inexpensive to purchase. It offers a great heating speed. However, it requires a lot of electricity.
The mixed boiler
The mixed boiler, or bi-energy or hybrid boiler, is equipped with two separate fireplaces to marry two energy sources or fuels. The combinations are multiple: oil/wood, coal/wood, and gas/solar, electric/solar. However, be aware of its imposing size, its high purchase price, and its maintenance cost.
Condensation or low temperature: which technology to choose?
In recent years, new technologies have emerged for boilers that are increasingly more efficient and less polluting. If you are changing boilers, now is the time to study these models, because they will also allow you to save energy.
Condensing boiler
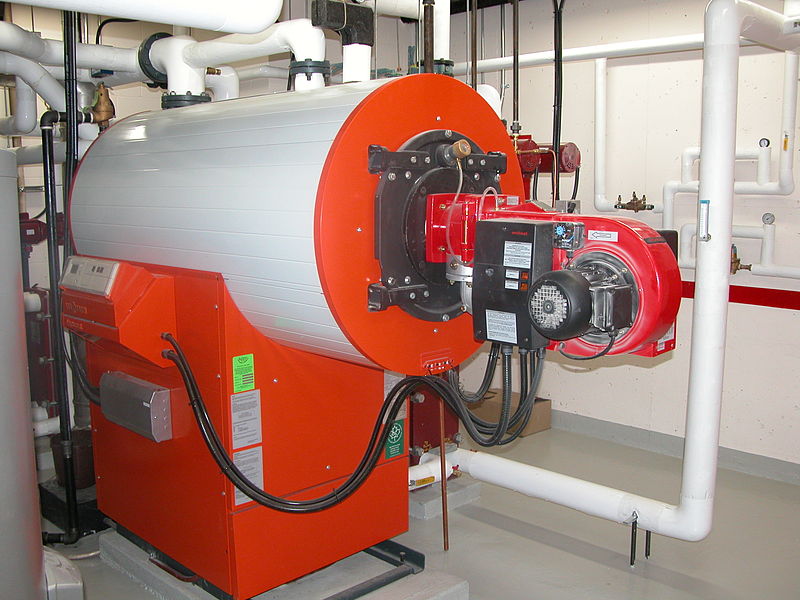

Its fuel consumption is reduced for an excellent performance. It allows a quicker return on investment, and the condensing-generation boiler model is even more advanced.
Low-temperature boiler
The boiler operates at lower temperatures. It can be fueled by gas or oil. Be careful; it only works with low-temperature radiators or underfloor heating.
You will be able to read more about it in our next publications:
– How a boiler works
– Criteria of choice
– Types of boilers: which energy to choose?
– Which technology to choose?