What Are the Different Types of Radiant Heating
All types of heating work on two principles: convection and radiation. Radiant heating is by far the most comfortable and energy efficient. Let’s look at the different heating systems that work with radiation and their particularities.
Radiant heating: radiation vs. convection
In the first case, the heating system heats the air in the room.
Since the warm air is lighter, this produces an air circulation: the heated air comes out of the top of the radiator; it circulates towards the top of the room and moves away from the heat source, “pushed” by the air coming out of the radiator.
This air gradually cools down, giving up its heat as it passes, and as it gets colder, it flows back down through the room until it passes through the radiator again and is heated up again.
Radiant heating
Radiation is the principle of the sun’s heat: it is a flow that heats the various surfaces it encounters, which will also radiate. The air is then heated by micro-convection on the heated surfaces.
Radiant heating, therefore, directly heats bodies, walls, and objects. We speak of “soft” heat when emitted at low temperatures because it provides a pleasant and rapid sensation of comfort, often very appreciated by the occupants.
Benefits of radiant heating
Radiant heating has only advantages over convection:
There is less air circulation, so there is less dust stirring.
The air is less likely to dry out.
The temperature the human body feels is the average between the air temperature and the room’s walls.
Any air circulation, even warm air, causes discomfort.
The temperature is more homogeneous, especially from top to bottom.
Examples of temperature stratification, i.e., temperature difference according to height*:
for radiators: 0°C to 0.8°C per meter, depending on the insulation of the building;
for convectors: 0.5°C to 1.2°C per meter, depending on the insulation of the building;
for low-temperature underfloor heating: 0°C per meter (for all buildings).
Different types of radiant heating
Here are the different types of radiant heating with their respective qualities, advantages, and disadvantages.
Water radiator
half of the heat is diffused by radiation;
good comfort;
choice of heat production.
Low-temperature water radiator/water floor heating
a higher proportion of radiation;
pleasant heat, good comfort;
choice of heat production;
higher heating efficiency in case of condensing boiler, solar heating, or heat pump,
Electric floor heating
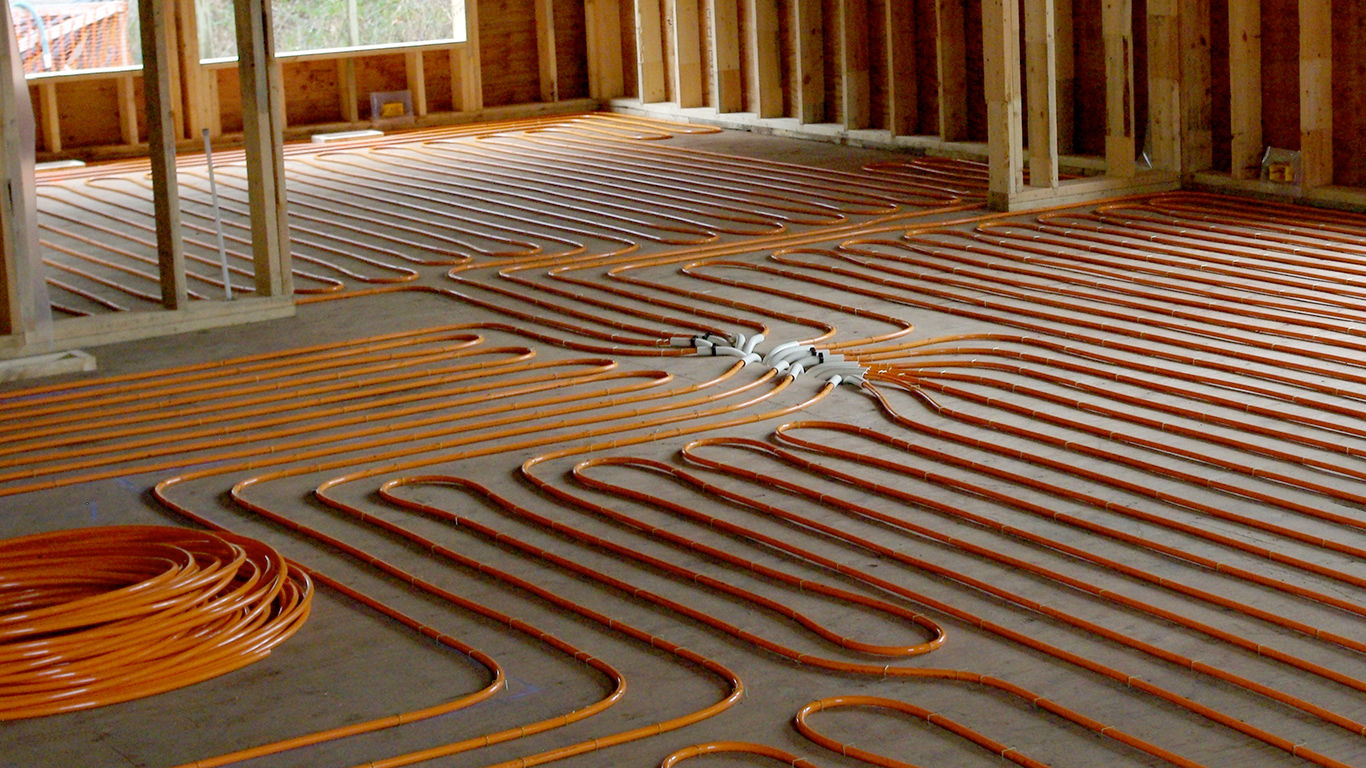

a high proportion of radiation;
pleasant heat, good comfort;
runs only on electricity, which has the disadvantage of being expensive and requiring a significant amount of primary energy (raw energy) for its manufacture.
Electric storage heater, inertia or heat transfer fluid
half or more of the heat is diffused by radiation;
fairly good comfort;
does not heat quickly, a large volume of emitters;
can be used to benefit from a night-time electricity rate;
works only with electricity, which has the disadvantage of being expensive and requiring a significant amount of primary energy (raw energy) for its manufacture.
Radiant panel (electric)
about half of the heat is diffused by radiation;
comfort depends on the temperature of the panel;
works only with electricity, which has the disadvantage of being expensive and requiring a significant amount of primary energy (raw energy) for its manufacture.
Stove, wood-burning stove, or pellet stove
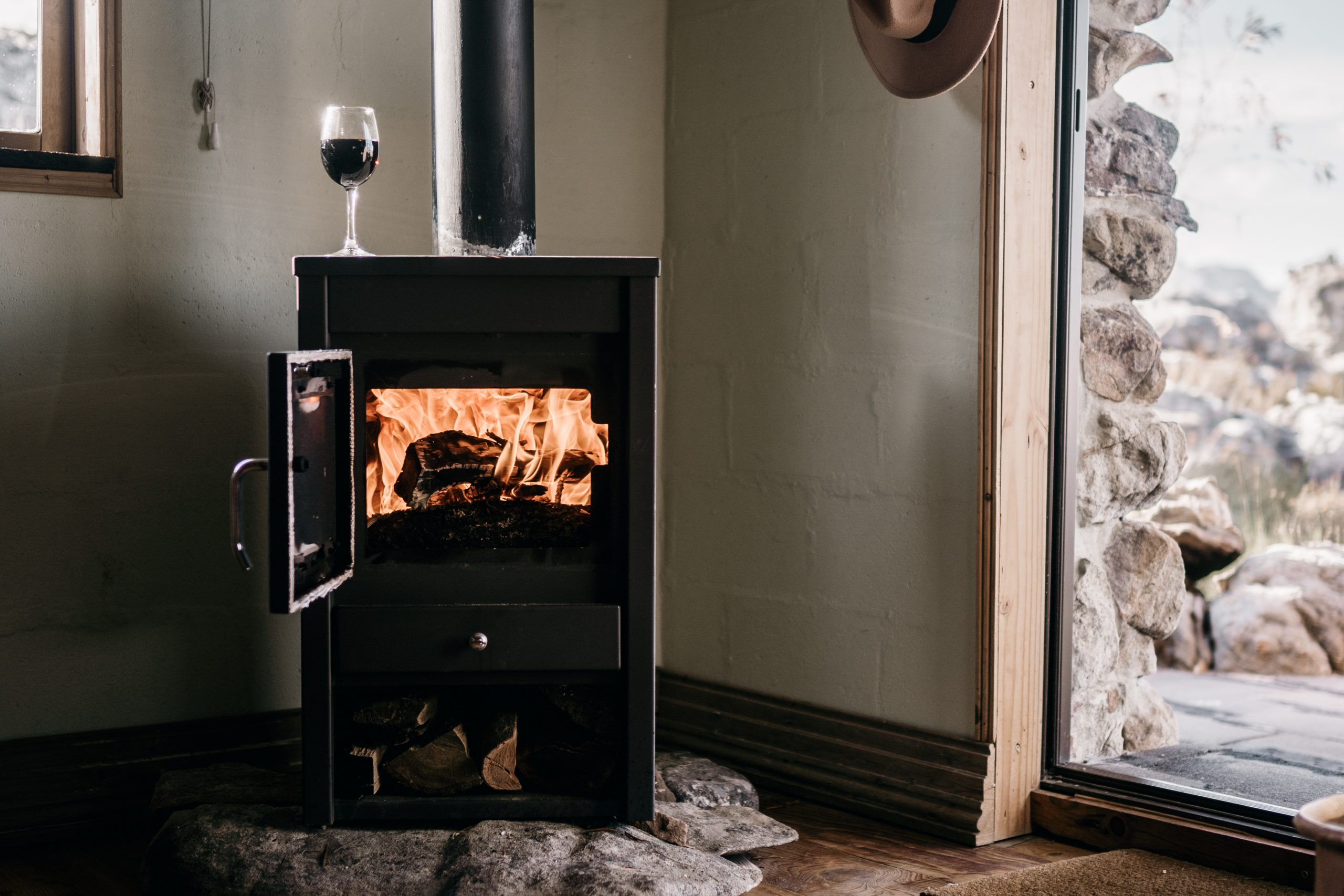

variable radiation (lower in the presence of hot air diffusion);
good comfort in the case of a central position of the device, sound insulation of housing, and the absence of a blower;
pleasant to have a wood fire;
need for a flue;
renewable and cheap energy source.
That’s it on the different types of radiant heating. Hope this post has provided you with the information you were looking for. Remember to jot down a few words in the comments below.